How to Diagnose and Treat Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a condition that occurs when the thyroid hormone levels are low in the body. Hypothyroidism occurs when your thyroid does not generate and release enough thyroid hormone into your body.
What is meant by thyroid?
Thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism. Your metabolism will slow down as a result, affecting your entire body. Underactive thyroid condition, often known as hypothyroidism, is quite common.
Generally common cases of hypothyroidism can be effectively treated with proper medications and the right care.
Are you experiencing symptoms of thyroid problems such as fatigue, weight gain, and hair loss? These signs could be indicative of hypothyroidism, a common thyroid disorder. In this comprehensive guide, let us explore the symptoms of thyroid problems, how to diagnose hypothyroidism, and the various treatment options available.
What are the common symptoms of thyroid problems?
Before delving into the diagnosis and treatment of hypothyroidism, it’s crucial to recognize the common symptoms of thyroid problems:
Fatigue: Unexplained fatigue is one of the primary symptoms of thyroid problems. People with hypothyroidism often feel tired, even after a full night’s sleep.
Weight Gain: Another common sign is unexplained weight gain, often accompanied by difficulty losing weight through diet and exercise.
Hair Loss: Hair loss or thinning can be caused by thyroid issues. Changes in hair texture and brittleness may also occur.
Cold Sensitivity: Feeling excessively cold, even in warm environments, is a symptom of thyroid problems frequently associated.
Dry Skin: Dry, itchy skin and brittle nails are typical skin-related symptoms of thyroid problems.
Muscle Weakness: Muscle aches, weakness, and cramps are common, making daily activities more challenging.
Depression and Mood Swings: Thyroid problems can affect mood, leading to feelings of depression, anxiety, and irritability.
Constipation: Sluggish bowel movements and constipation are gastrointestinal symptoms of thyroid problems.
Irregular Menstruation: Women may experience irregular menstrual cycles and heavier periods.
Hoarseness: A hoarse voice and difficulty swallowing can be a symptom of thyroid problems. If you are experiencing any of these signs visit an endocrinology hospital to get proper care and treatment.
What are the various steps involved in diagnosing hypothyroidism?
If you suspect you have hypothyroidism due to the symptoms of thyroid problems mentioned above, it’s essential to seek a proper diagnosis. The following procedures are frequently used to diagnose hypothyroidism:
Clinical examination: A healthcare provider will start by conducting a thorough physical examination and discussing your medical history. Mention all symptoms of thyroid problems you’ve been experiencing. Family history of thyroid disorders may also be considered.
Blood examinations: The primary diagnostic tool for hypothyroidism is a blood test that measures thyroid hormone levels. The two crucial thyroid hormones are:
Thyroid stimulating hormone function: Elevated TSH levels often indicate an underactive thyroid, as the body produces more TSH to stimulate the thyroid gland when hormone levels are low.
Thyroxine: Total and free T4 levels are checked to assess thyroid function. Low T4 levels in conjunction with high TSH levels are indicative of hypothyroidism.
Thyroid antibody tests: These tests help determine if an autoimmune condition like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is causing hypothyroidism.
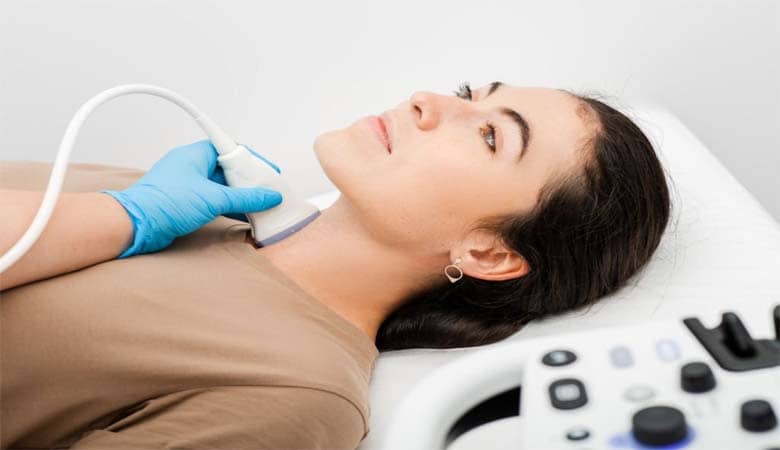
Ultrasound: An ultrasound of the thyroid gland may be performed to assess its size and check for any nodules or abnormalities.
What are the best treatment options for hypothyroidism?
Once a diagnosis of hypothyroidism is confirmed, treatment options are available to manage the condition effectively. The goal of treatment is to restore normal thyroid hormone levels and alleviate the symptoms of thyroid problems.
Thyroid hormone replacement therapy: The most common and effective treatment for hypothyroidism is thyroid hormone replacement therapy. This involves taking synthetic thyroid hormones, typically in the form of a synthetic medication. The medication is usually taken orally once a day, and the dosage is adjusted based on individual needs and response to treatment.
Constant monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor your progress and adjust medication dosages as necessary. Blood tests, especially measuring TSH levels, help ensure that thyroid hormone levels are within the optimal range.
Lifestyle modifications: In addition to medication, certain lifestyle changes can complement the treatment of hypothyroidism and alleviate symptoms of thyroid problems:
Diet: Eating a well-balanced diet rich in nutrients like iodine and selenium can support thyroid health. Limiting the consumption of goitrogenic foods (which can interfere with thyroid function) may also be beneficial.
Exercise: Regular physical activity can help boost metabolism and alleviate fatigue associated with hypothyroidism.
Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate thyroid problems, so practicing stress-reduction techniques such as meditation and yoga can be helpful.
Adequate Sleep: Prioritizing good sleep hygiene can combat fatigue and improve overall well-being.
Medical surgery:In rare cases, surgical removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy) may be necessary, particularly if there are thyroid nodules, goiter, or other structural abnormalities.
Know your supplements: Certain medications and supplements can interfere with the absorption of thyroid hormone replacement medication. Inform your healthcare provider about all medications and supplements you are taking to ensure they do not affect your thyroid treatment.
Can hypothyroidism be completely cured?
Yes, there is a treatment available for the majority of Hashimoto’s hypothyroidism instances. With an individualized treatment strategy that incorporates dietary adjustments, vitamins, stress management, peptide therapy, and thyroid medicines, patients can totally overcome hypothyroidism.
Can hypothyroidism be passed genetically?
The chance of acquiring hypothyroidism is higher for first-degree relatives of people with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Hashimoto’s is the primary reason when it comes to hypothyroidism.
Important Takeaway:
If you suspect you have hypothyroidism based on the symptoms of thyroid problems you are experiencing, seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial for managing this thyroid disorder effectively. With thyroid hormone replacement therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and regular monitoring, individuals with hypothyroidism can lead healthy, symptom-free lives and regain their vitality and well-being. Reach out to a thyroid specialist if you are facing any hypothyroidism issues.